Programming Tool - Python
Technique - Genetic Algorithm
Firestation Problem Modeling
District X has 42 small towns (towns 1 to 42). The district council is in the process of determining the locations of building fire stations to serve the community of these 42 towns.
The district council has limited fund and the council wants to build the minimum number of fire stations. Each town is a potential place where a fire station can be located.
List of variables
Problem formulation
The goal of this assignment is to determine the minimum fire stations to be built in order to serve all the towns such that the driving time between town is less or equal than the maximum driving times. The objective (1) is to minimize the number of fire station built. Constraint (2) and (3) are to ensure at least one town built with fire station is within a specific driving times of each town.
The problem is formulated in a linear programming:
Representation
A binary representation is used to represent the fire station set covering problem where the length of the chromosome equals the total number of towns in the distinct which is 42. 1 in the first gene means the fire station will built in town 1. Figure 1.1 shows an example of a chromosome solution in which the total number of towns is 10 and the fire station will be built in town 1, 5, 8 and 10.
Here is an example of binary representation chromosome:
Methodology
Since the problem to be solved involve a large search place as we have 42 towns so we need to search through all 242 . Therefore, Genetic algorithm (GA) is used to solve the set covering problem.
Import dataset
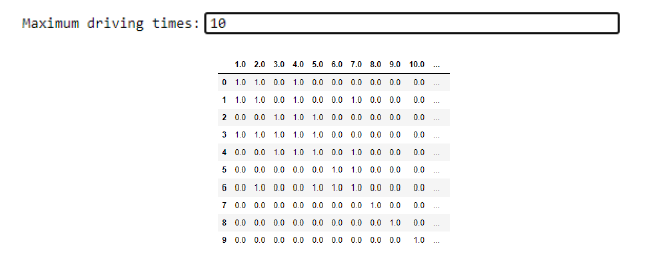
First the dataset of each driving time between towns is imported and a 42x42 coverage matrix is created where 1 means the driving time between town is within the maximum driving time and 0 otherwise. Figure below shows an example of first 10 rows and columns of the matrix, if the input maximum driving time value is 10 minutes meaning we need to find the minimum number of fire station to be built in a town that can cover all the towns within 10 minutes. The matrix showed 1 in the first row of second column means the driving time between town 1 and town 2 is within the maximum driving time; 10 minutes.
1
2
3
4
5
arrivetown = np.linspace(1,42,num=42)
times = pd.read_csv('drivingtime.csv',names=arrivetown)
minTime = float(input("Maximum driving times:"))
times[times<=minTime] = 1
times[times>minTime] = 0
Initialization
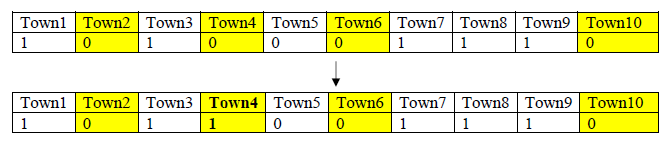
The individual solution is generated randomly with value 0 and 1. Since we need to satisfy the constraint (3) which is to make sure at least one fire station location is within the driving time of each town. There is a condition when generate the population. The value 1 need to assign randomly on the indexes of the chromosome (towns) which can cover a specific town. For example, if only the fire station built in town 2, 4, 6, and 10 can cover town 2. The value 1 need to be assign randomly on either 2, 4, 6 or 10 Here is the figure to illustrate this more clearly showing an example of a randomly generated solution:
Since the randomly generated solution has all 0 for town 2, 4, 6, and 10. It is not feasible because town 1 could not be covered so the value 1 will be put randomly on either 2, 4, 6 or 10. So the value 1 is put on gene no 4 in this example.
Here is the code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def populations(popsize,chromosome_length,times):
population=([[random.randint(0,1) for x in range(chromosome_length)] for i in range(popsize)])
population = np.array(population)
#constraint to ensure at least 1 town
for i in range (popsize):
for j in range(chromosome_length):
arrivetown = times[times[j=1]==1].index.tolist()
population[i][random.choice(arrivetown)]=1
return population
Fitness calculation
The objective function is the total number of towns that need to build a fire station. To ensure a feasible solution, any solution that violate the constraints or involve repetitive towns will impose a penalty P.
Objective function = $\sum_{i=1}^m x_i + P$
The penalty involves two criteria:
First criteria– A penalty will be added to the objective function if the solution generated has repetitive town covered, a penalty value of the total number of repetitive towns will be added to the objective function.
1
2
3
4
#if there are repetitive town penalty will be imposed
penalty = 0
penalty += (len(firestation[population])-len(set(firestation[population])))
objvalue += penalty
Second criteria - A value of 10 will be added to the objective function if at least one town not covered. This can happen after crossover or mutation, the constraint (3) can be violated so a high penalty needs to be imposed to ensure the algorithm will not choose this solution.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#if there is at least one town not covered penalty of 10 will be imposed
if len(set(firestation[population]))==42:
penalty+=0
objvalue+=penalty
fitness.append(objvalue)
else:
penalty+=10
objvalue+=penalty
fitness.append(objvalue)
Here is the overall code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
def fitnessCal(chromosome,times):
firestation=[]
fitness=[]
for population in range (chromosome.shape[0]):
firestation.append([])
objvalue=0
for gene in range (chromosome.shape[1]):
if chromosome[population,gene]==1:
objvalue = objvalue+1
for d in range(len(times)):
if times.iloc[d,gene]==1:
firestation[population].append(d)
else:
continue
else:
continue
#if there are repetitive town penalty will be imposed
penalty = 0
penalty += (len(firestation[population]) - len(set(firestation[population])))
objvalue += penalty
#if there is at least one town not covered penalty of 10 will be imposed
if len(set(firestation[population])) ==42:
penalty +=0
objvalue+=penalty
fitness.append(objvalue)
else:
penalty+=10
objvalue+=penalty
fitness.append(objvalue)
return fitness
Selection
Two parent chromosomes are selected from the best of two randomly selected chromosomes in the population N = 10 to perform crossover and produce two child chromosomes. The child chromosomes will be added to the populations and the new population now has N = 20 solutions and are sorted in ascending order. The new population will then pick the first 10 solutions which is the best 10 solutions with the minimum objective value as a new population. Since our objective is to minimize the objective function.
Here is the code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
def parent_selection(population,scores):
#Get population size
population_size = len(scores)
#Pick individuals for tournament
sol_1 = random.randint(0,population_size-1)
sol_2 = random.randint(0,population_size-1)
#Get fitness score for each
sol_1_fitness = scores[sol_1]
sol_2_fitness = scores[sol_2]
#Identify individual with highest fitness
if sol_1_fitness >= sol_2_fitness:
winner = sol_1
else:
winner = sol_2
#Return the chromosome of the winner
return population[winner,:]
Crossover
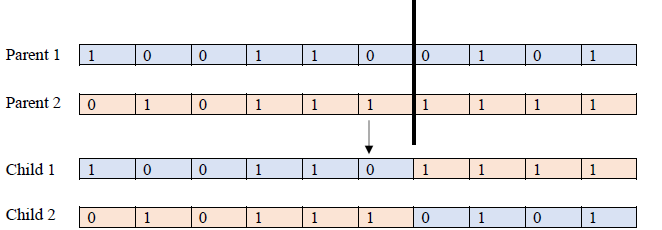
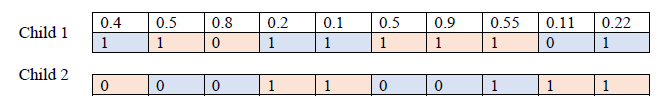
The crossover step involves selecting two parent chromosomes to generate two child chromosomes. A single point crossover and uniform crossover will be used.
This is an example of single point crossover:
Here is the code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def crossover(parent_1,parent_2):
#Get length of chromosome
chromosome_length = len(parent_1)
#Pick crossover point, avoiding ends of chromosome
crossover_point = random.randint(1,chromosome_length-1)
#Create children
child_1 = np.hstack((parent_1[0:crossover_point],parent_2[crossover_point:]))
child_2 = np.hstack((parent_2[0:crossover_point],parent_1[crossover_point:]))
return child_1, child_2
In uniform crossover if the random value is less than 0.5, the gene is copy from parent 1 whereas if the random value is equal or greater than 0.5, gene is copy from parent 2.
This is an example of uniform point crossover:
Here is the code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def crossover(parent_1,parent_2):
P = np.random.rand(len(parent_1))
for i in range (len(P)):
if P[i] < 0.5:
temp = parent_1[i]
parent_1[i] = parent_2[i]
parent_2[i] = temp
child_1 = np.array(parent_1)
child_2 = np.array(parent_2)
return child_1, child_2
Mutation
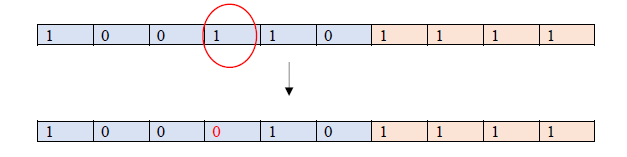
Mutation step is performed on randomly alter selected genes. Single point bit flip mutation is used. Thus, one bit is selected and then flip it. If the selected bit is 0 then turn it to 1 and if the selected bit is 1 then turn it to 0.
Here is an example of mutation of a chromosome:
Here is the code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def mutation(chromosomes,pm):
for i in range(chromosomes.shape[0]):
if(random.random()<pm):
int_random_value = random.randint(0,chromosomes.shape[1]-1)
if chromosomes[i,int_random_value] == 0:
chromosomes[i,int_random_value] = 1
else:
chromosomes[i,int_random_value] = 0
else:
continue
return chromosomes
Termination
The solution terminates after 100 fitness function evaluation. 10 number of generation and 10 population size.
Genetic algorithm instances
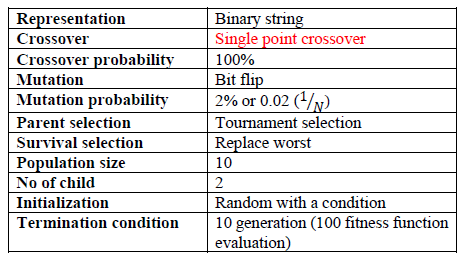
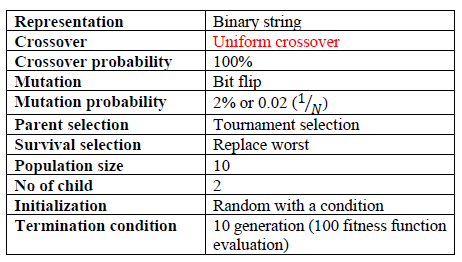
Parameter tuning is performed on the type of crossover. Thus, there are two Genetic algorithm (GA) instances where one instance used a single point crossover while another instance used uniform crossover as shown in the following:
Instance 1:
Instance 2:
Results
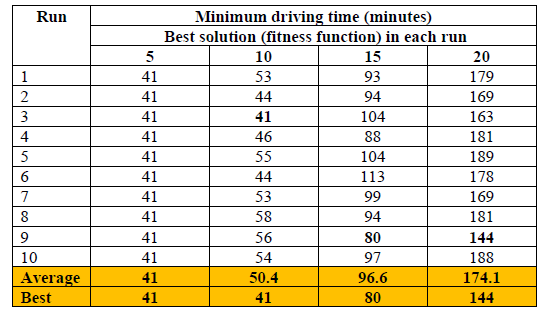
The result using single point crossover (Instance 1):
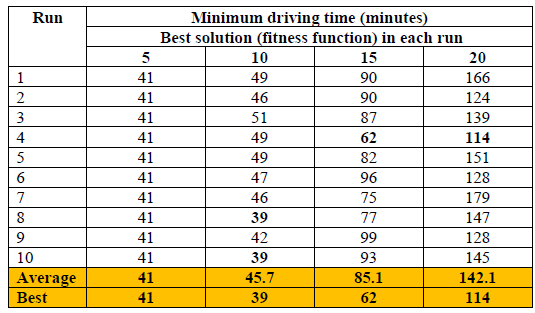
The result using uniform point crossover (Instance 2):
Since our objective is to minimize the objective function. The GA instance of using uniform crossover (Instance 2) has a better result than using single point crossover (Instance 1). The average objective value of GA Instance 2 for all the scenario (5, 10, 15, 20 minutes) are less than GA Instance 1. Therefore, uniform crossover is performed better in this problem.
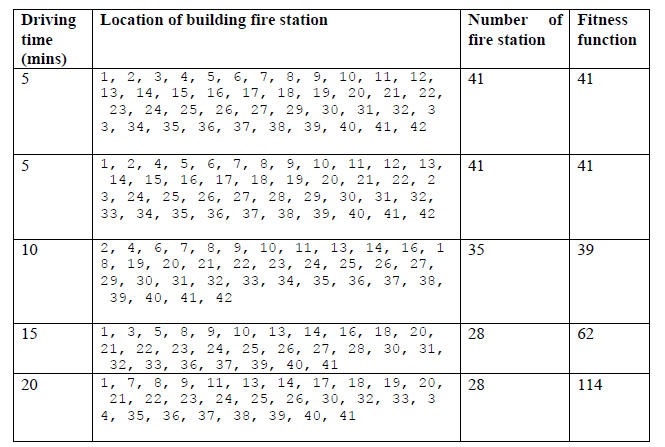
The district council should build firestation as following based on different driving time: